|
|
|
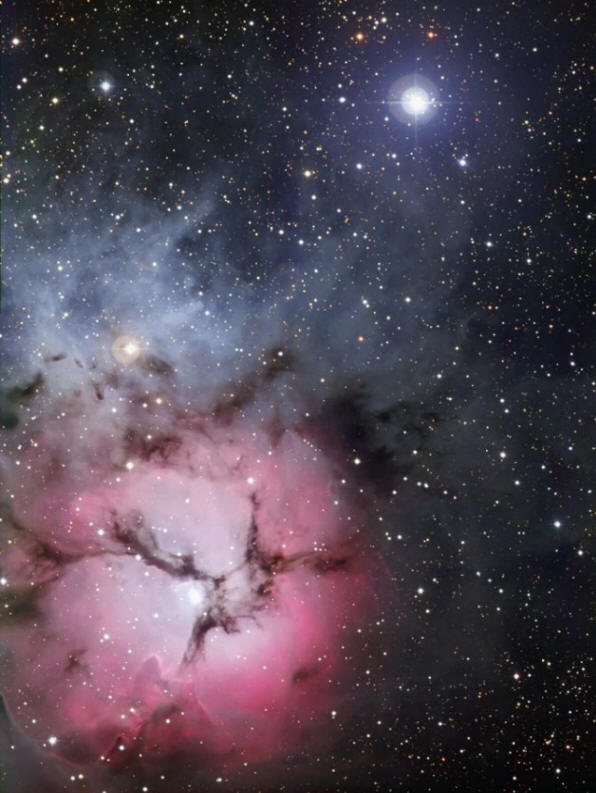

The Trifid Nebula. Credit: ESO/Chandra X-ray
Observatory.
The Trouble with the Trifid
Mar
23, 2010
What is reasonable is often
determined by what is familiar,
traditional, consensual.
Before space probes and adaptive
optics, all that astronomers had to
study were twinkles in the night
sky. So astronomy was almost
entirely theoretical—twinkles in the
mind’s eye. There were few
opportunities to test the conceptual
twinkles in a laboratory.
Space probes took the laboratories
to the planets and to the spaces in
between. New “optics” removed the
twinkling and “looked” with all the
wavelengths of the electromagnetic
spectrum. The steady glare of data
revealed the errors of the
theoretical twinkles in astronomers’
eyes…but the familiarity, tradition,
and consensus had crystallized in
astronomical institutions like
silver grains on a photographic
plate: The old theories continued to
twinkle in the eyes and to outshine
the new twinkle in the skies.
Tradition twinkles again in the
press release for ESO’s latest
image of the Trifid Nebula. Turning
a blind eye on a century’s research
into the properties of
plasma, the press release
describes the nebula as
“gas...heated by hundreds of
scorching young stars until it emits
the red signature light of
hydrogen..., just as hot neon gas
glows red-orange in illuminated
signs....” Neon signs are, of
course, plasma powered by
electricity, and they are “hot” only
in the sense of being electrified,
not because they are “scorching.”
A similar twinkle of tradition
obscures astronomers’ vision of the
blue region at the top of the image.
It’s called a “reflection nebula,”
in which “dusty gas scatters the
light from nearby, Trifid-born
stars.” This explanation was
reasonable, or at least familiar,
when reflection was the only
mechanism known for producing
polarized light that had a spectrum
similar to nearby stars. Later, the
invention of the synchrotron
contributed
another possibility: blue
polarized emissions of field-aligned
electric currents twisting along
magnetic fields.
The dark filaments that divide the
nebula into thirds, hence giving it
its name, Trifid, are called “gases
and dust.” They will “collapse and
form new stars” due to “gravity’s
inexorable attraction.” This twinkle
of explanation is entirely pretense.
It’s contradicted not only by
observations but also by traditional
theory itself: Clouds of gas can
collapse only if they have no
angular momentum and no magnetism.
However, for “some unknown reason,”
all such clouds do have angular
momentum and magnetism, usually a
lot. As one astronomer has
commented, “Astronomy has a spin
problem.”
This is not a problem when the
electrical properties of plasma are
recognized: Birkeland currents
generate spin, and the z-pinch
effect is efficient at coalescing
matter into filaments, disks, and
dense spherules. One plasma
physicist has called Birkeland
currents the “vacuum cleaners of
space.”
The traditional pretense of
gravitational collapse then follows
Alice’s rabbit into the wonderland
of “rising density, pressure and
temperature inside these gaseous
blobs will eventually trigger
nuclear fusion, and yet more stars
will form.” Arthur Eddington, who
proposed the internal thermonuclear
power source for stars nearly a
century ago, may be forgiven for his
pretentiousness.
That Birkeland currents can transmit
electrical power over interstellar
and intergalactic distances was not
yet known. Just as earlier
astronomers had imagined the Sun to
be a large campfire and then a large
coal fire because those were
familiar sources of light and heat,
so Eddington could be expected to
bring the newly discovered source of
thermonuclear fusion reactions into
the fold of the familiar. If he had
been friends with Thomas Edison or
Irving Langmuir instead of with
Albert Einstein, he might have got a
different twinkle in his eye,
one that would have complemented
instead of contradicted the space
age discoveries.
The final twinkle of the press
release is the “finger of gas
pok[ing] out from the cloud,
pointing directly at the central
star.... This is an example of an
evaporating gaseous globule….” From
a plasma point of view, it’s an
example of a stellar-scale comet—but
not the familiar consensus-comet of
sublimating dirty snow: it’s an
electrical discharge
sheath formation in the galactic
current that powers the nebula. The
stars that form in the tiny centers
of the discharge pinches gain the
notice of our eyes with their
twinkling, but they are the least
important of the vast
electromagnetic structures in the
plasma that fills what we
traditionally call the vacuum of
space.
Mel Acheson
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
YouTube video, first glimpses of Episode Two in the "Symbols of an Alien Sky"
series.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Three ebooks in the Universe Electric series are
now available. Consistently
praised for easily understandable text and exquisite graphics.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|