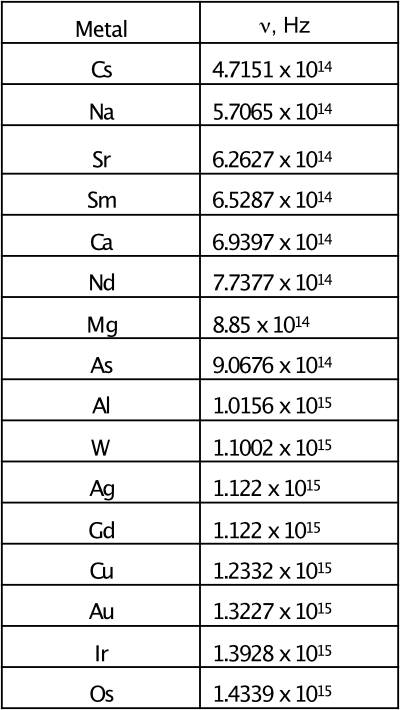
2. Gravitational and electromagnetic waves differ only in their wavelengths.
3. The Sub-photon is the newly introduced particle that is the building block for construction of both gravitational and electromagnetic waves.
4. Sub-photon is the particle that is the building block of elementary subatomic particles.
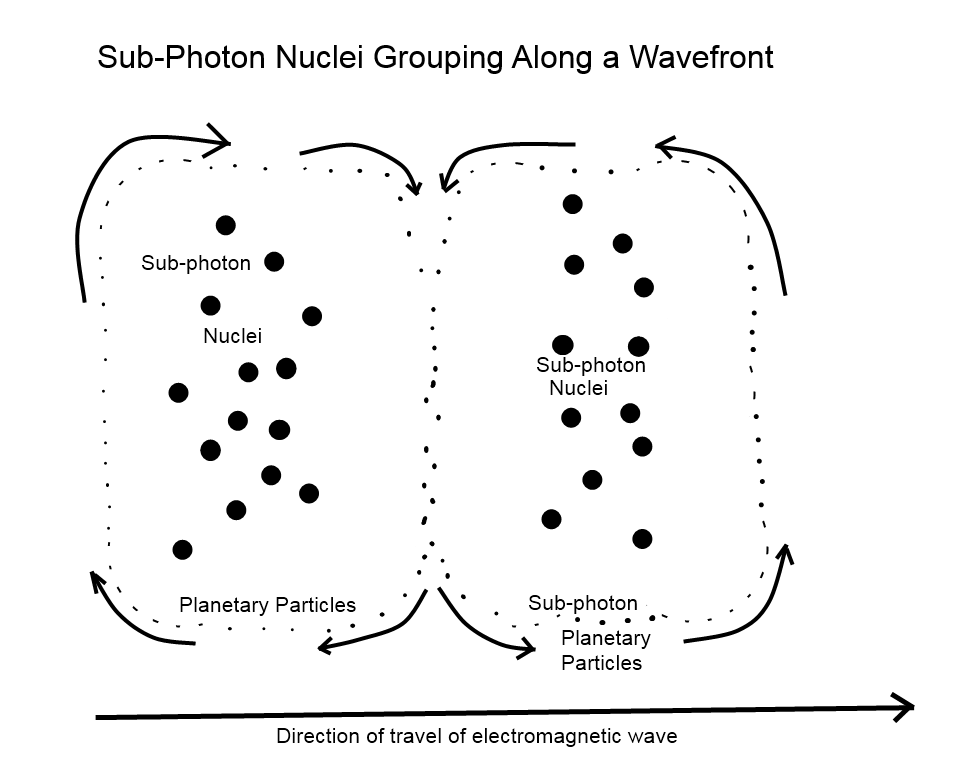
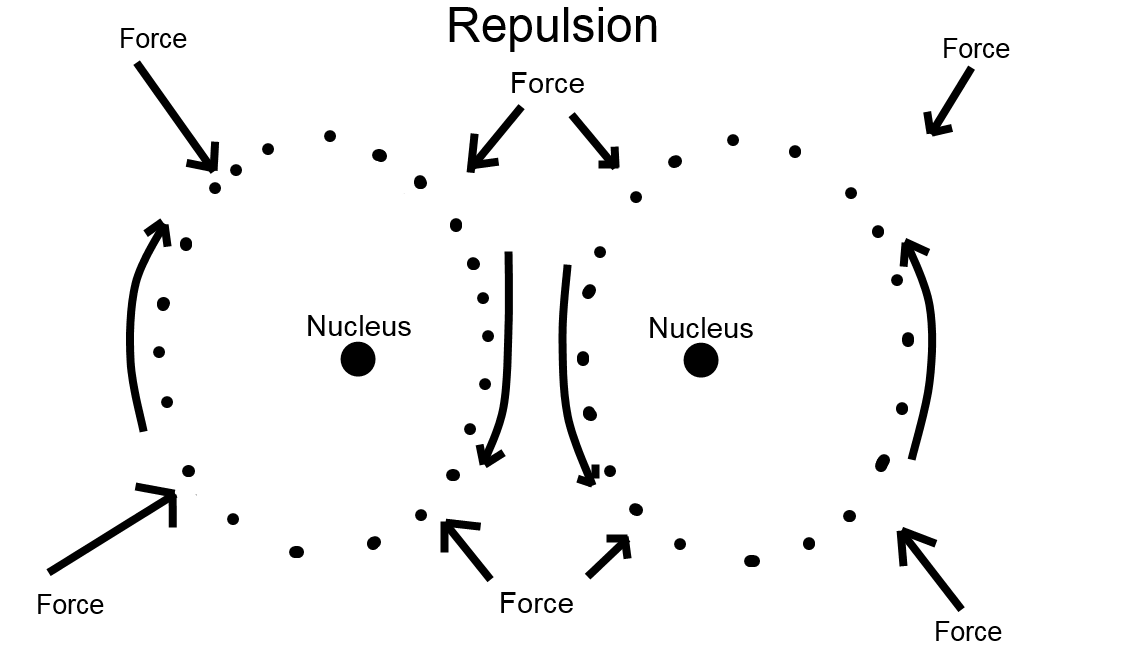
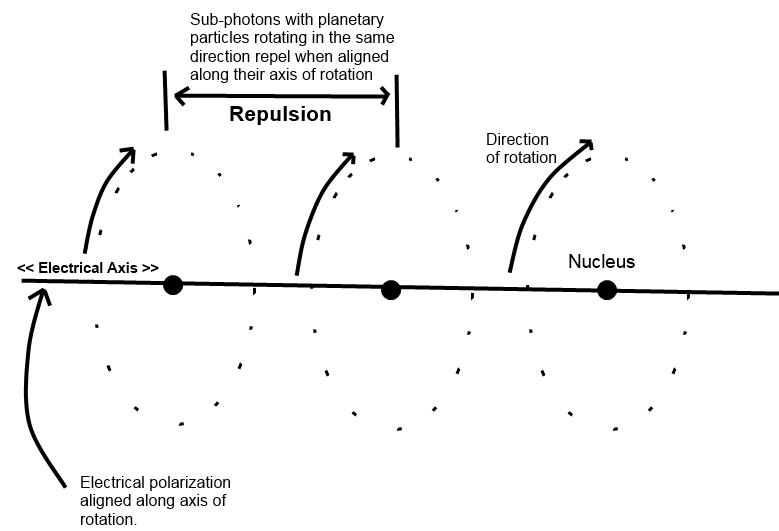
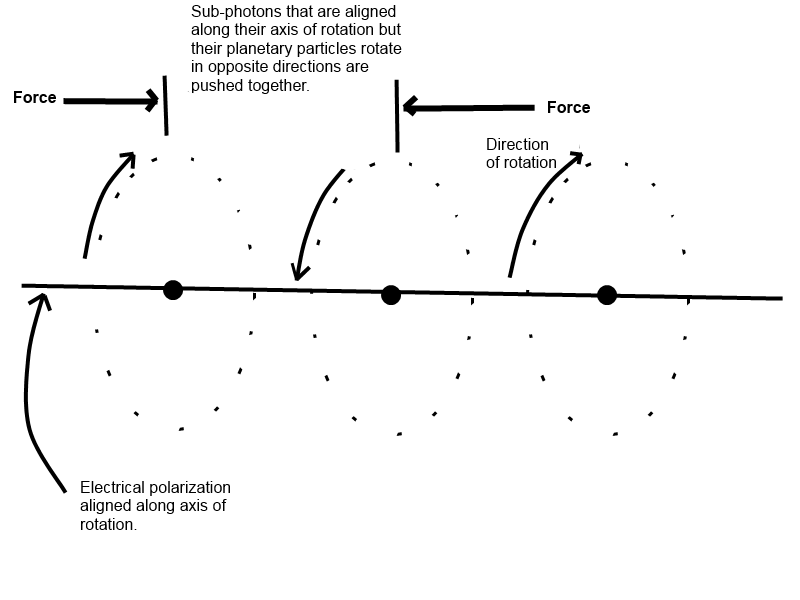
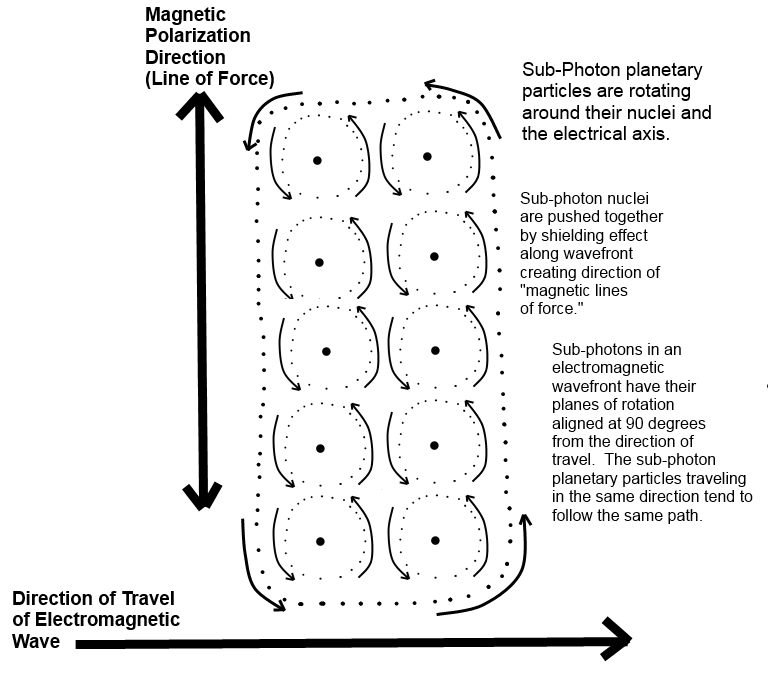
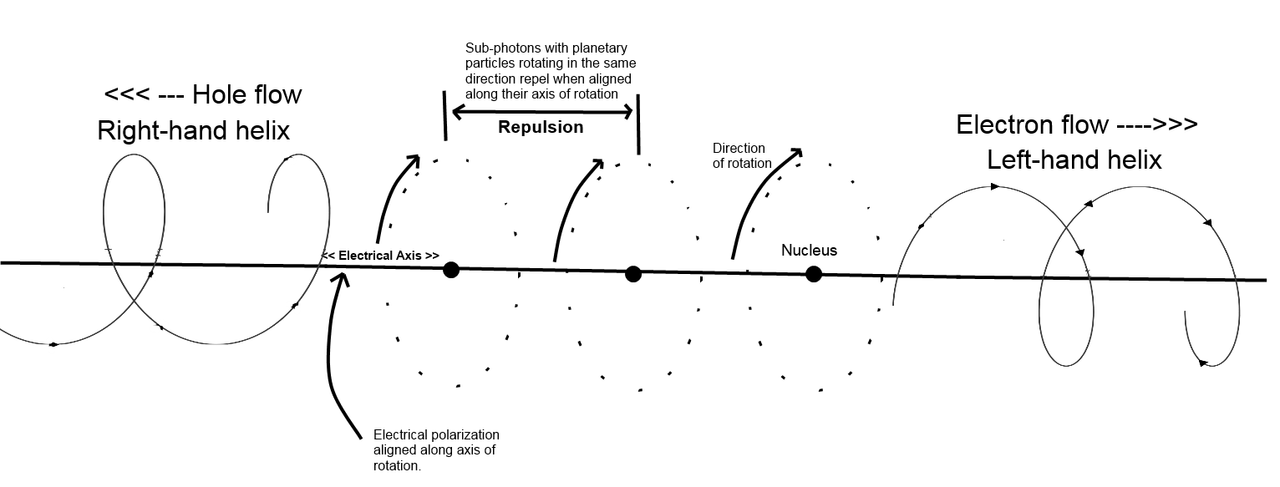
5. A sub-photon consists of a nucleus (sun) particle and rotating planetary particles.
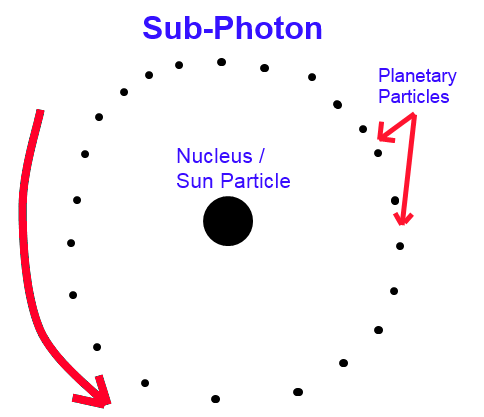
Electromagnetic Waves:
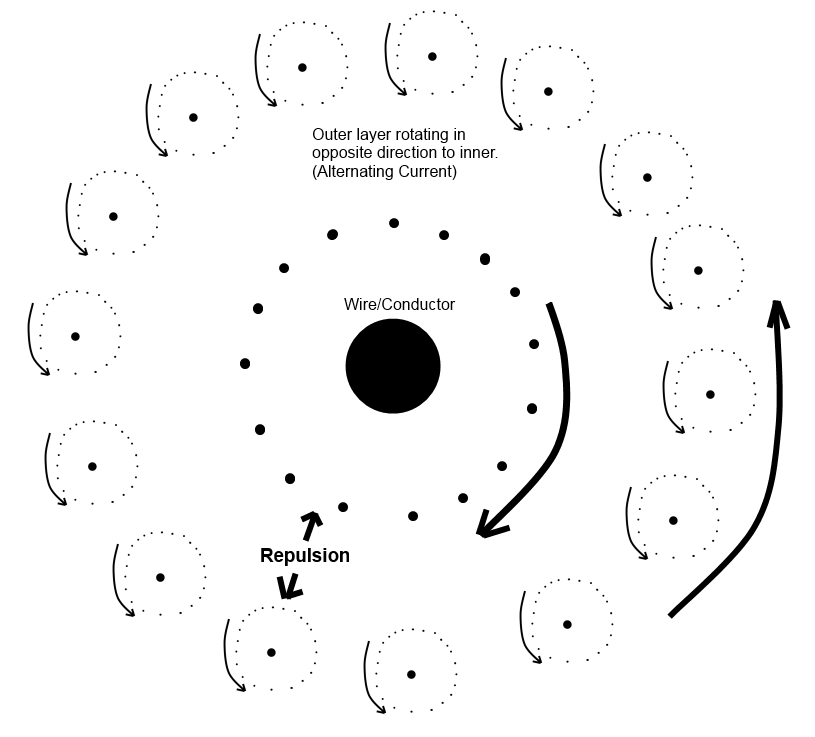
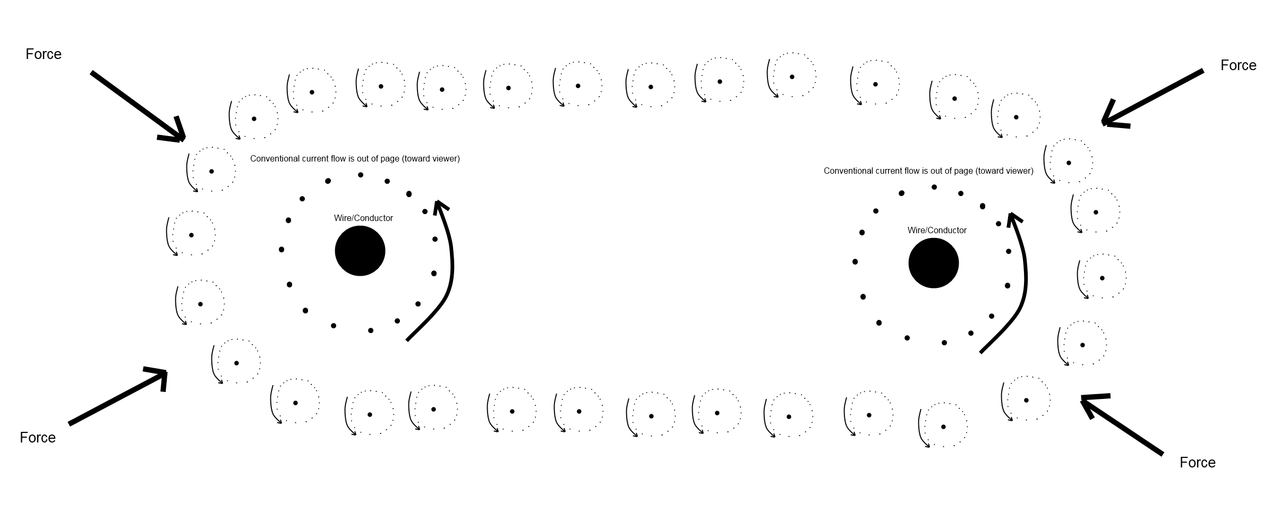
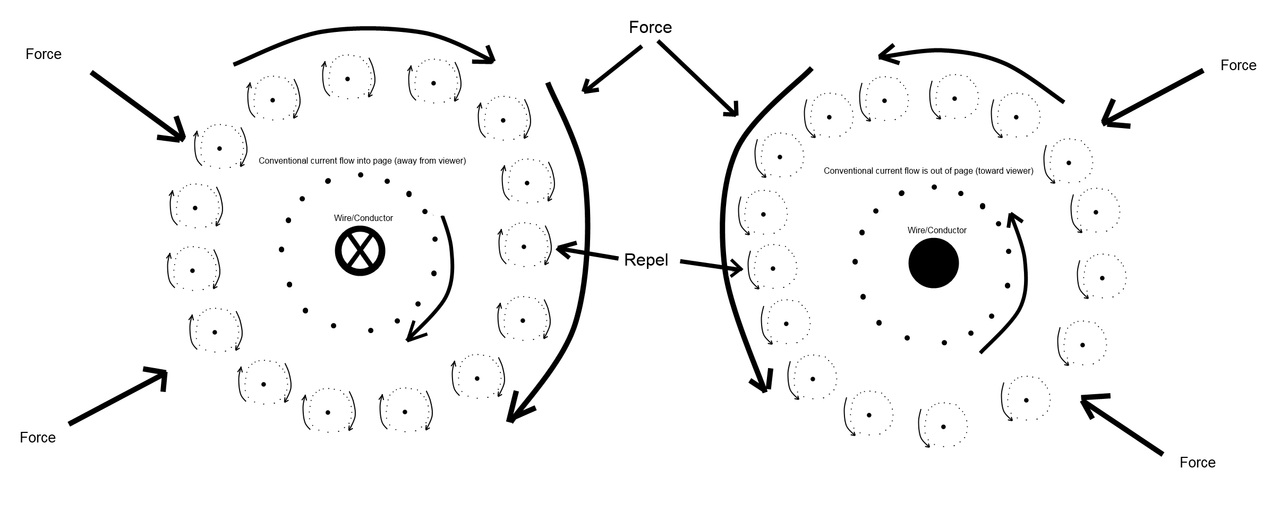
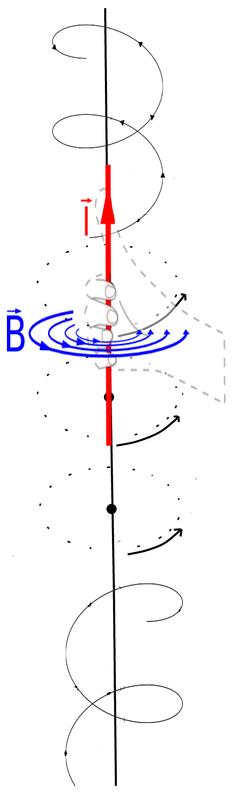
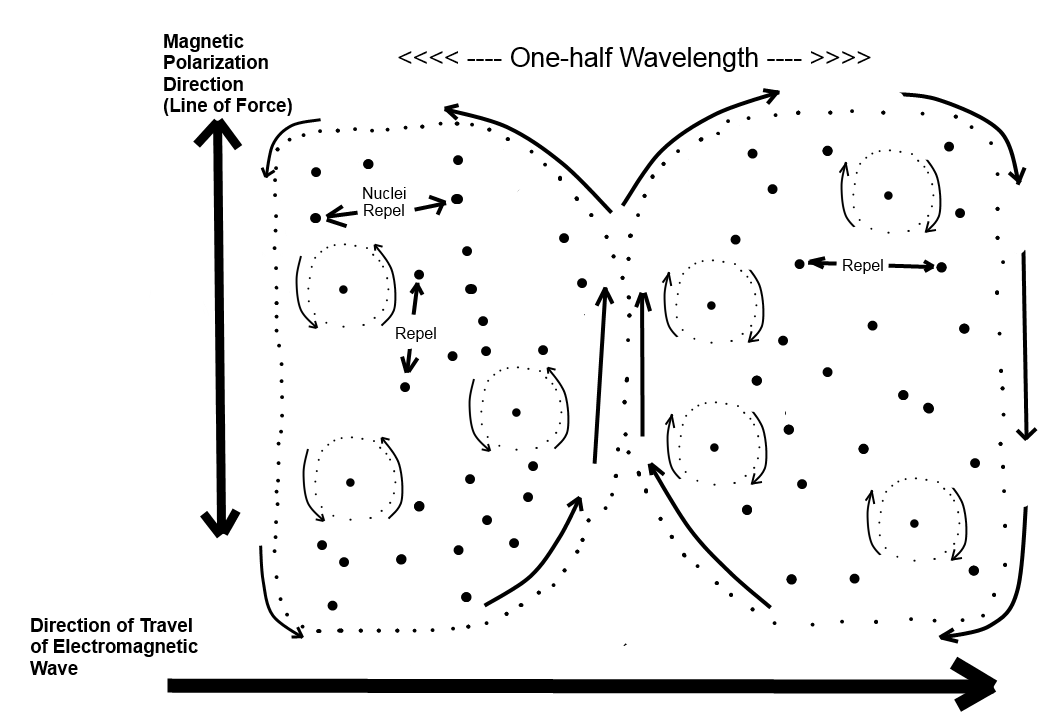
1. Traveling sub-photons that are polarized (rotating) in alternating directions create both electromagnetic waves and gravitational waves.
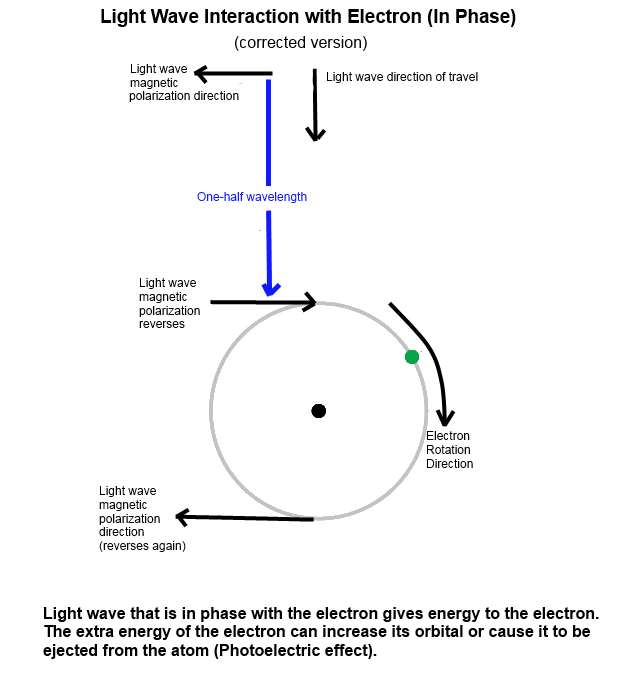
2. Electromagnetic waves have a (typically shorter) wavelength that resonates with atoms or larger objects.
3. Sub-photon particles of electromagnetic waves originating in space have poor penetration into celestial objects compared to gravitational waves and predominantly resonate with atoms in the outer layers (atmosphere, crust) of celestial bodies. They tend to exert a force (radiation pressure) there.
4. Electromagnetic waves typically have a higher electromagnetic frequency than gravitational waves.
5. If an electromagnetic wave encounters matter and does not resonate, it can exert a weak radiation pressure, giving electromagnetic waves a similar weak interaction to a lower frequency gravitational wave.