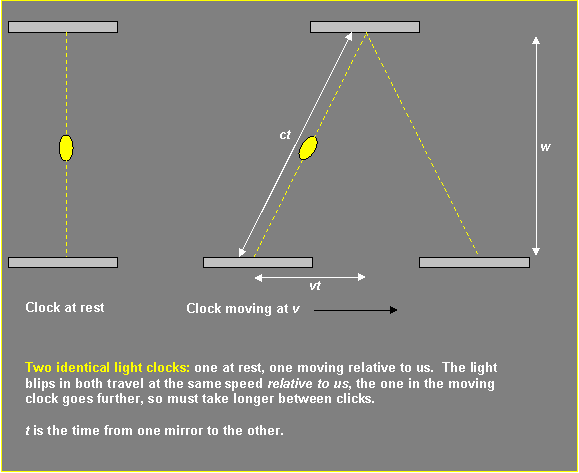
Time Dilation, as proposed by the "observation" of light clocks.

- light clock classic.gif (5.6 KiB) Viewed 17676 times
The above diagram is fairly representative of the classic method used to "reason" on the idea of time dilation.
The argument being that an observer standing next to his light clock (i.e. in the same frame of reference) would "see" the left-hand clock. But another, relative moving, observer would "see" the same light clock as the right-hand version and conclude that because the light pulse/beam/ray travels further, it takes longer and so "time" appears to be slowed down or "dilated".
First, some details about the construction of the light-clock need to be made clear:
- The space between the mirrors is a perfect vacuum. So the speed of the light-pulse is constant and no scattering occurs whatsoever.
- One of the mirrors, let's choose the bottom one, has a laser mounted below it that initiates the pulse through its semi-mirrored surface.
- Also mounted on the surface of the mirror is a detector that registers the pulse as it passes through the surface of the mirror and also registers the reflected signal.
- We will assume that once initiated the light-pulse continues back and forth between the mirrors with no losses to the mirrors or detector
- The detector is linked to a light bulb or a display showing a numerical count that are activated and incremented each time the detector registers the light-pulse.
The Real Scenario:
The light pulse proceeds upwards towards the top mirror. When it reaches the top mirror, the electrons at the surface "absorb" the "light-signal" and emit a new light-signal that is a facsimile of the incident light-signal - we refer to this as light reflection. This new light pulse travels back to the bottom mirror and is detected. The time between consecutive detections defines the rate of the light-clock. As the light pulse travels in a perfect vacuum there is absolutely no scattering of the light-pulse, so nobody, absolutely nobody and no other matter, whether in the same "reference frame" or anywhere else in the universe, receives any information whatsoever about the progress of the light-pulse. In other words, there is no observer anywhere at all that can "see" the light-pulse. The only way to observe the light pulse, would be to stick your head inside the light clock so that the light pulse enters your eye, but of course that would interfere with its operation. In order to observe the rate of the light-clock, the detector is linked to a light-bulb that flashes every time the detector registers the light pulse and a count display that increments at each detection. In fact, we could reduce the opportunity for confusion still further by enclosing the light clock in an opaque covering.
By pointing out that, in reality, the light-pulse is not visible to any observers, and then removing that distraction completely by enclosing the light-clock, there is now no light-pulse path length distance to confuse the gullible. The rate at which the light-clock operates is presented purely as a function of the flashing bulb or a display showing a numerical count of the pulses. Both the "local frame" observer and a remote relatively moving frame observer would see the light-bulb flash at exactly the same rate. and the display counter update at exactly the same rate. There is absolutely no logic, or even any proposed reality distortion field (or should that be relativity distortion field), that suggests that the two observers would not receive the information about the flashing bulb and count display, and hence also about the functioning of light-clock, at exactly the same rate.
Furthermore, everything in the universe is travelling. There is no matter that is not travelling. Therefore, the left-hand clock never ever ever happens. The right-hand clock is the only possible scenario; and that's completely regardless of its "stationary" or "moving" assignment. Some people might disagree with this, relativists certainly will, but that is because they have allowed themselves to believe that time, distance and light signals are magic. However, even by the loose reasoning of relativity, there is nothing to suggest that the distance between the mirrors would change or contract with a forward motion perpendicular to the mirror faces (as presented in the diagram). So for the light pulse to always continue to bounce between the mirrors, it must under all circumstances be aimed diagonally toward where the "next" mirror will be. And this angle will have to be continuously adjusted to match the velocity of the mirrors. As the mirrors move faster, the distance the light-pulse has to travel increases and the so the light-clock runs slower.
With the elimination of the gross misinterpretation of the observed view of the light-clock operation, we are left with single consecutive events common to all observers. There is no alternative interpretation that can be applied to the flashing of the bulb or the display counter. When the bulb flashes a light-signal is transmitted both to the local observer, moving with the light-clock, and to all and any remote observers. Obviously, relatively moving observers will experience a Doppler shift corresponding to their relative velocity, but that is not time dilation as proposed by relativity. All observers must see the flashing bulb at precisely the same rate (allowing for Doppler shift) and there is no other interpretation available to disagree with this conclusion.
Just in case you object to the covered light-clock, let's now consider a "visible" light-clock as close as is possible to as originally conceived. However, as I have already pointed out there are issues with the standard description of this "thought" experiment. The first and most obvious, is that what one is told one would "see", is not what would actually be observed. In order to make the operation of the light-clock visible we could fill it with smoke so as to scatter the beam/pulse toward observers. Obviously, we must then posit that the smoke will have so effect on the light-pulse other than to make it visible to observers. Now if an observer views the light-clock from in front or behind, with reference to the direction of travel, they will "see" the left-hand light-clock image. Any observer viewing the light-clock from the side, with reference to the direction of travel, will see the right-hand light-clock image. Furthermore, from in front or behind, the light-pulse will appear to be travelling slower than c, although this point is merely academic. Anyhow, the rate at which the light-pulse completes a lap of the light-clock must intrinsically and unarguably correspond with the rate of the bulb flashing. The important point is that all observers must also receive information about the light-pulse at the same rate and without any hint of time "dilation".
Whether the standard interpretation of this thought experiment is a childish mistake or a deliberate deception is unclear, but in either case it is baffling how this ever passed scrutiny. What is clear however, is that any theoretical model that somehow distorts the reasoning of this thought experiment to arrive at "time dilation", is either dishonest or in gross error.
Michael